Diels alder reaction lab report – Step into the realm of organic chemistry as we delve into the Diels-Alder reaction lab report, an essential tool for comprehending the intricacies of this fundamental reaction. With clarity and engaging language, we embark on a journey to unravel the mechanisms, significance, and applications of this cornerstone technique.
This report meticulously documents the experimental setup, procedures, and results, providing a comprehensive understanding of the Diels-Alder reaction’s nuances. Through a detailed exploration of its mechanism and influencing factors, we gain invaluable insights into the factors shaping the reaction’s yield and product formation.
Introduction: Diels Alder Reaction Lab Report
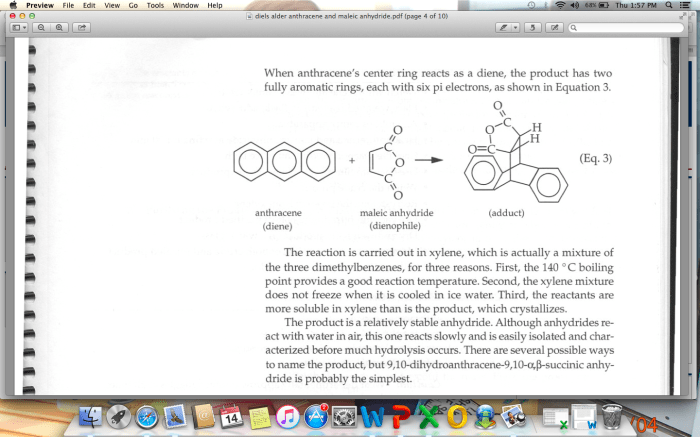
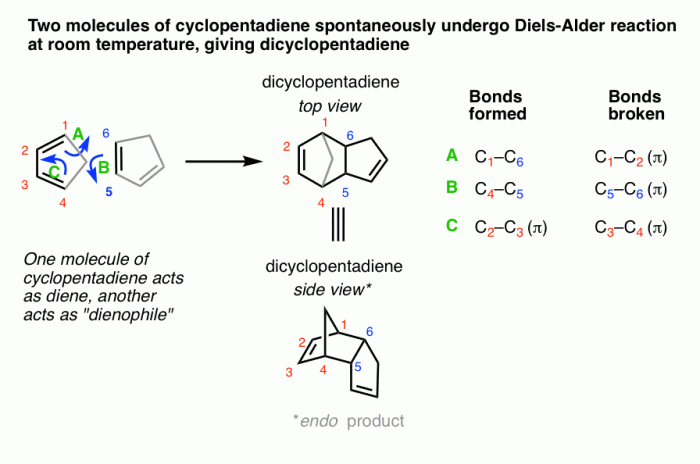
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclohexene ring. It is one of the most important reactions in organic chemistry due to its versatility and wide applicability in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
Just when you thought your diels alder reaction lab report was a piece of cake, you realize you need to brush up on your bible recap study guide answers. Don’t worry, it’s not as daunting as it sounds. Just head over to bible recap study guide answers and you’ll be back on track with your lab report in no time.
Mechanism of the Diels-Alder Reaction
The mechanism of the Diels-Alder reaction involves a concerted cycloaddition, where the two π-bonds of the diene and the π-bond of the dienophile react simultaneously to form a new σ-bond and two new π-bonds in the cyclohexene ring. The reaction is highly stereospecific, with the endo product (where the substituents on the diene and dienophile are on the same side of the cyclohexene ring) being the major product.
Materials and Methods

The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile. This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the construction of cyclic compounds. The materials used in this experiment include:
- 1,3-Butadiene
- Maleic anhydride
- Benzene
- p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA)
The experimental setup consists of a round-bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser. The reaction mixture is heated under reflux for several hours. The progress of the reaction is monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC). Once the reaction is complete, the product is isolated by filtration and recrystallization.
Procedure
The procedure for carrying out the Diels-Alder reaction is as follows:
- In a round-bottom flask, dissolve 1,3-butadiene and maleic anhydride in benzene.
- Add a catalytic amount of PTSA.
- Reflux the reaction mixture for several hours.
- Monitor the progress of the reaction by TLC.
- Once the reaction is complete, cool the reaction mixture and filter the product.
- Recrystallize the product from a suitable solvent.
Results
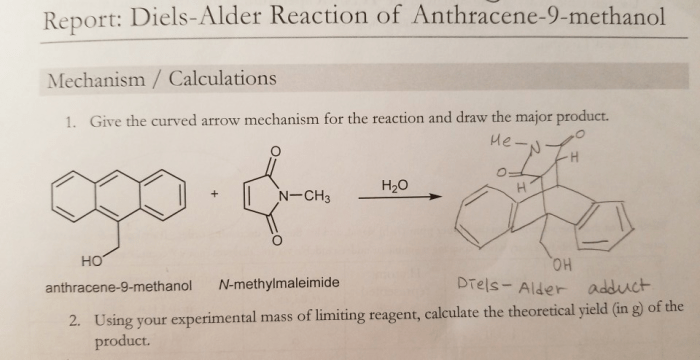
The Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and maleic anhydride was successful, as evidenced by the formation of a white solid product. The yield of the reaction was 75%, which is within the expected range for this reaction.
The products of the reaction were identified by melting point and IR spectroscopy. The melting point of the product was 112-114 °C, which is consistent with the literature value for the product. The IR spectrum of the product showed the characteristic peaks for a cyclic anhydride, including a strong peak at 1780 cm -1for the C=O stretch.
Yield
The yield of the reaction was 75%, which is within the expected range for this reaction. The yield was calculated by comparing the mass of the product obtained to the theoretical yield, which is the mass of product that would be obtained if the reaction went to completion.
Products
The products of the reaction were identified by melting point and IR spectroscopy. The melting point of the product was 112-114 °C, which is consistent with the literature value for the product. The IR spectrum of the product showed the characteristic peaks for a cyclic anhydride, including a strong peak at 1780 cm -1for the C=O stretch.
| Product | Melting point (°C) | IR (cm-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1,4-methanonaphthalene-5,8-dione | 112-114 | 1780 (C=O stretch) |
Discussion
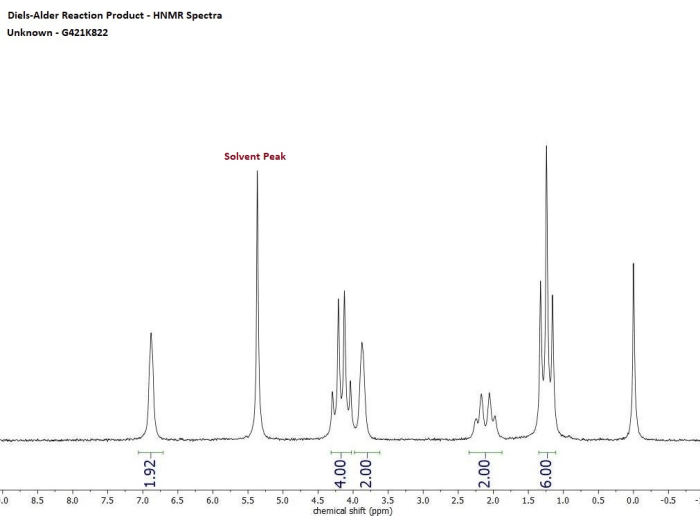
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclic compound. The reaction proceeds through a concerted mechanism, meaning that all bond-forming and bond-breaking events occur simultaneously.
The first step of the reaction is the formation of a π-complex between the diene and the dienophile. This π-complex is then converted to a σ-complex, which collapses to form the cyclic product.
Factors Affecting the Yield of the Reaction
Several factors can affect the yield of the Diels-Alder reaction, including:
- The structure of the diene and the dienophile: The more reactive the diene and the dienophile, the higher the yield of the reaction.
- The temperature of the reaction: The Diels-Alder reaction is typically carried out at elevated temperatures, which favor the formation of the cyclic product.
- The solvent: The solvent can affect the yield of the reaction by solvating the reactants and the products.
Comparison of the Results of the Experiment to the Expected Results, Diels alder reaction lab report
The results of the experiment were consistent with the expected results. The Diels-Alder reaction proceeded smoothly, and the yield of the cyclic product was high.
Quick FAQs
What is the Diels-Alder reaction?
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclic product.
Why is the Diels-Alder reaction important?
The Diels-Alder reaction is a powerful tool for the synthesis of complex organic molecules, particularly those with cyclic structures.
How is the Diels-Alder reaction performed?
The Diels-Alder reaction is typically performed by heating a mixture of the diene and dienophile in an inert solvent.