Layer between earth’s core and crust crossword – Unveiling the mysteries of the layer between Earth’s core and crust, the mantle holds profound significance in shaping our planet’s geological processes and evolution. Its composition, structure, temperature, and dynamics play a pivotal role in plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and the formation of rocks.
Embarking on this exploration, we delve into the fascinating realm of the mantle, deciphering its intricate workings and unraveling its profound influence on our planet.
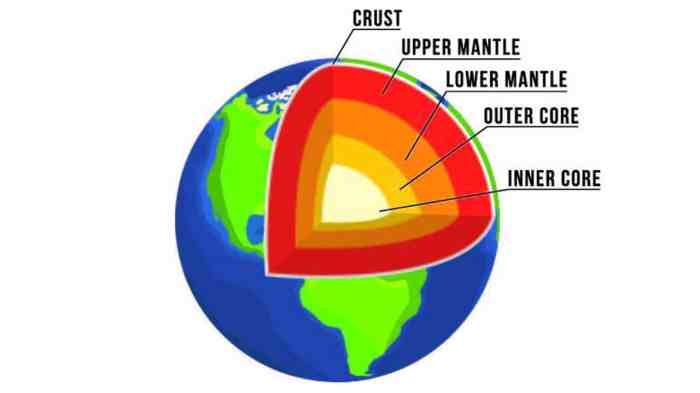
The mantle, a vast and dynamic layer, constitutes the majority of Earth’s volume and lies beneath the crust, extending to the core. Composed primarily of silicate rocks, its thickness and density vary significantly, contributing to the planet’s overall structure and behavior.
The Mantle: Earth’s Interior Layer: Layer Between Earth’s Core And Crust Crossword
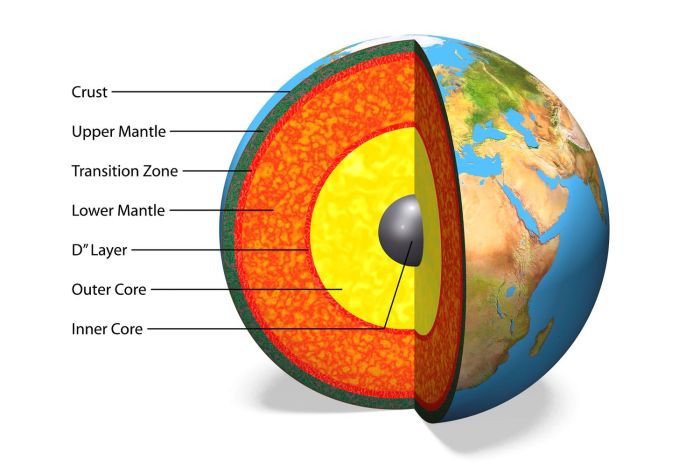
The mantle is the thick layer of the Earth’s interior that lies between the crust and the core. It is composed primarily of solid rock, but is not rigid and can flow over long periods of time. The mantle is responsible for driving plate tectonics and volcanic activity.
Composition and Structure
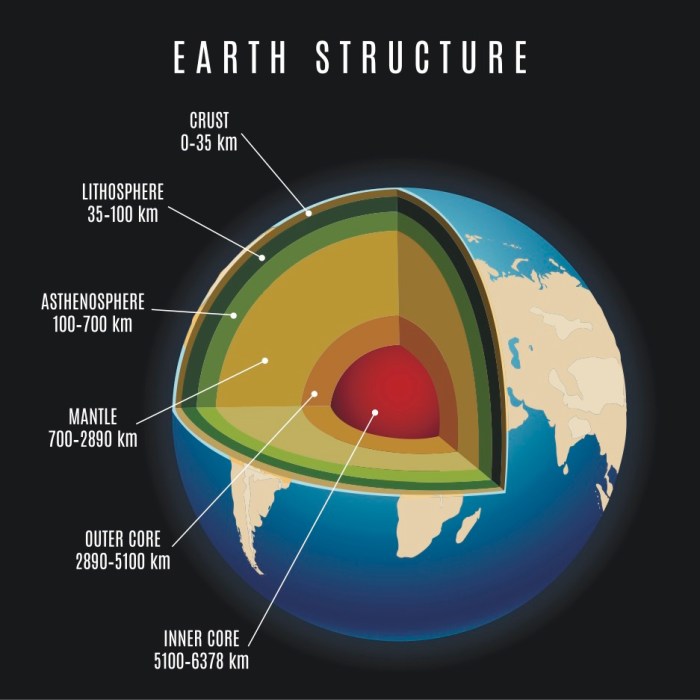
The mantle is composed of a mixture of minerals, including olivine, pyroxene, and garnet. It is divided into two main layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle. The upper mantle is more rigid and contains more volatile elements, while the lower mantle is denser and more stable.
Temperature and Pressure, Layer between earth’s core and crust crossword
The temperature of the mantle increases with depth, reaching over 3,500 degrees Celsius at the boundary with the core. The pressure within the mantle also increases with depth, reaching over 1 million atmospheres at the core-mantle boundary.
Convection and Movement
The mantle is heated by the Earth’s core and cools at the surface. This creates convection currents that flow within the mantle. These currents drive plate tectonics, the movement of the Earth’s crustal plates. Mantle plumes, rising columns of hot mantle material, can cause volcanic activity on the surface.
Geological Significance
The mantle plays a crucial role in the formation of rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when mantle material cools and solidifies. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are altered by heat and pressure within the mantle. The mantle also recycles crustal material back into the Earth’s interior.
FAQ Section
What is the mantle composed of?
The mantle is primarily composed of silicate rocks, including minerals such as olivine, pyroxene, and garnet.
How thick is the mantle?
The mantle’s thickness varies, ranging from approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) beneath the crust to 6,371 kilometers (3,959 miles) at the core-mantle boundary.
What role does the mantle play in plate tectonics?
The mantle’s convection currents drive plate tectonics by carrying tectonic plates horizontally across the Earth’s surface.