People in societies where assertiveness is low – In societies where assertiveness is low, individuals face unique challenges in expressing their thoughts and needs. This introductory paragraph delves into the cultural influences and communication patterns that shape these societies, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic.
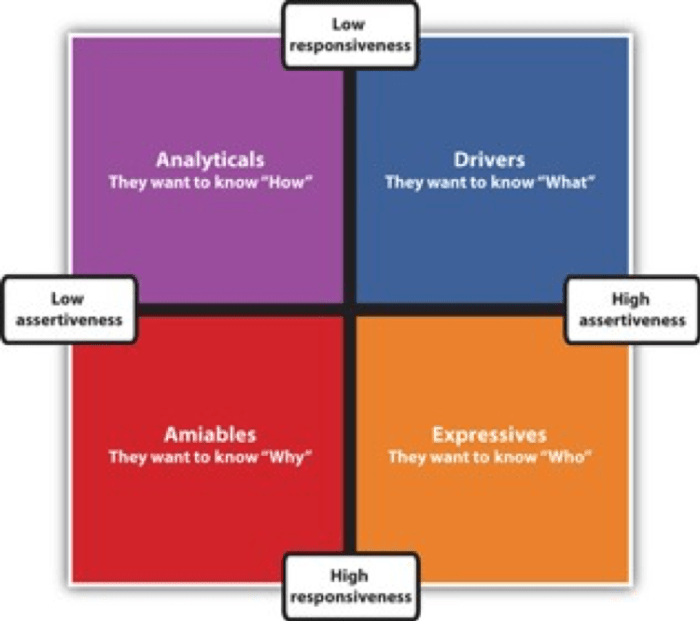
Cultural values and norms play a significant role in shaping assertiveness. In societies where collectivism and harmony are prioritized, individuals may be discouraged from expressing their opinions or asserting their needs for fear of disrupting group cohesion. Conversely, in individualistic societies, assertiveness is often seen as a positive trait, allowing individuals to advocate for themselves and pursue their goals.
Cultural Influences on Assertiveness
Cultural values and norms play a significant role in shaping assertiveness. In societies that emphasize collectivism, interdependence, and harmony, individuals may be less assertive to avoid disrupting group dynamics. Conversely, in individualistic cultures that prioritize self-expression and autonomy, assertiveness is often valued and encouraged.
For example, in Japan, where collectivism is deeply ingrained, people tend to be more indirect and avoid direct confrontation. In contrast, in the United States, an individualistic society, assertiveness is generally seen as a positive trait.
Communication Patterns in Low-Assertiveness Societies, People in societies where assertiveness is low
In societies with low assertiveness, communication styles often reflect the cultural values that emphasize harmony and avoidance of conflict. Individuals may use indirect language, such as hinting or suggesting, to express their thoughts and feelings.
Hesitation and reluctance to speak up are also common in low-assertiveness societies. People may avoid expressing their opinions or disagreeing with others to maintain social cohesion.
Social Consequences of Low Assertiveness
Low assertiveness can have negative consequences for both individuals and society as a whole. Individuals with low assertiveness may experience reduced self-esteem, difficulty expressing their needs, and missed opportunities.
In society, low assertiveness can hinder effective communication, decision-making, and problem-solving. It can also create a culture of passivity and conformity, where individuals are less likely to challenge the status quo or speak up for their rights.
Factors Contributing to Low Assertiveness
Low assertiveness can be influenced by various psychological and environmental factors. Fear of conflict, social anxiety, and learned helplessness are common psychological factors that contribute to low assertiveness.
In addition, environmental factors such as cultural norms, family dynamics, and peer pressure can also shape an individual’s assertiveness.
Strategies for Enhancing Assertiveness
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Practice assertiveness | Engage in role-playing or simulations to practice assertive behavior in different situations. |
| Build self-confidence | Identify and focus on strengths and accomplishments to boost self-esteem and confidence. |
| Manage anxiety | Use relaxation techniques or cognitive restructuring to reduce anxiety and fear associated with assertive behavior. |
Questions Often Asked: People In Societies Where Assertiveness Is Low
What are the common communication patterns observed in low-assertiveness societies?
In low-assertiveness societies, communication tends to be indirect, hesitant, and conflict-avoidant. Individuals may use vague language, avoid eye contact, and rely on non-verbal cues to express their thoughts and feelings.
How does low assertiveness impact individuals?
Low assertiveness can lead to reduced self-esteem, difficulty in expressing needs, and missed opportunities. Individuals may struggle to stand up for themselves, assert their boundaries, or pursue their goals.