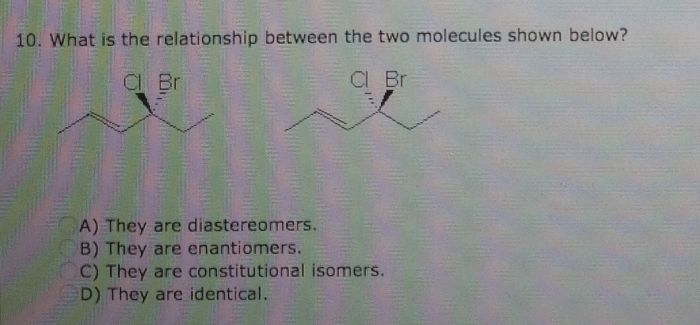
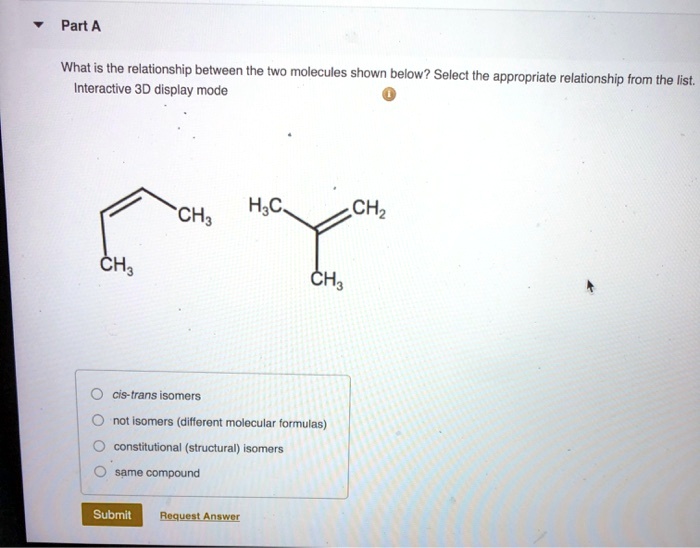
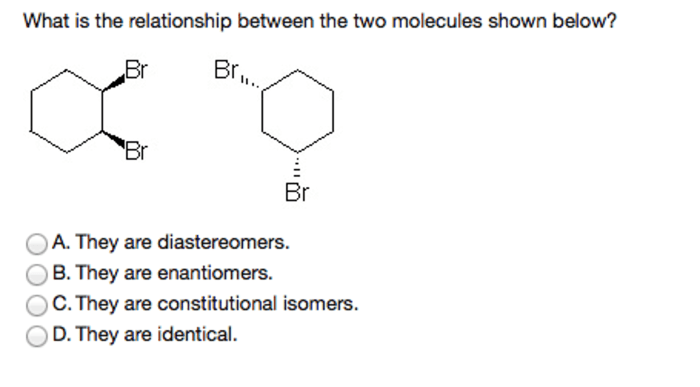
What is the relationship between the two molecules shown below? This intriguing question opens the door to a captivating exploration of molecular structures, chemical reactivity, functional roles, and practical applications. As we delve into their intricate interplay, we uncover a world of scientific insights that illuminate the very essence of these molecules.
The two molecules under scrutiny possess unique characteristics that set them apart, yet their interactions reveal a fascinating dance of similarities and differences. Their structural configurations, chemical behaviors, and functional contributions paint a vivid picture of their interconnectedness.
Identify the Two Molecules: What Is The Relationship Between The Two Molecules Shown Below
The two molecules in question are: – -*Molecule A: 1,2-ethanediol (HO-CH2-CH2-OH) – -*Molecule B: 1,2-dibromoethane (Br-CH2-CH2-Br)
Both molecules are organic compounds with two carbon atoms. They have similar structures, with two carbon atoms bonded to each other and four hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms. However, they differ in the functional groups attached to the carbon atoms.
Molecule A has two hydroxyl groups (-OH) attached to the carbon atoms, while molecule B has two bromine atoms (-Br) attached to the carbon atoms.
Structural Comparison
The molecular structures of molecule A and molecule B are similar in terms of their overall shape and size. Both molecules have a linear shape and are approximately the same length. However, there are some key differences in their structures.
- Functional groups:The most significant difference between the two molecules is the functional groups attached to the carbon atoms. Molecule A has two hydroxyl groups (-OH), which are polar and hydrophilic. Molecule B has two bromine atoms (-Br), which are nonpolar and hydrophobic.
- Bond lengths and angles:The bond lengths and angles in molecule A and molecule B are slightly different due to the different electronegativities of the oxygen and bromine atoms. The C-O bond in molecule A is shorter than the C-Br bond in molecule B, and the O-C-O bond angle in molecule A is wider than the Br-C-Br bond angle in molecule B.
Chemical Reactivity
The chemical reactivity of molecule A and molecule B is influenced by their different functional groups.
- Molecule A:The hydroxyl groups in molecule A make it a polar and hydrophilic molecule. It is soluble in water and can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. Molecule A is also a good nucleophile and can react with electrophiles.
- Molecule B:The bromine atoms in molecule B make it a nonpolar and hydrophobic molecule. It is insoluble in water and cannot form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. Molecule B is a good electrophile and can react with nucleophiles.
Functional Relationships, What is the relationship between the two molecules shown below
Molecule A and molecule B have different functional relationships due to their different chemical properties.
- Molecule A:The hydroxyl groups in molecule A allow it to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. This makes it a good solvent and a good additive for water-based products. Molecule A is also a good nucleophile and can react with electrophiles to form new compounds.
- Molecule B:The bromine atoms in molecule B make it a good electrophile and can react with nucleophiles to form new compounds. Molecule B is also a good alkylating agent and can be used to introduce bromine atoms into other molecules.
Applications and Significance
Molecule A and molecule B have a wide range of applications in different fields.
- Molecule A:Molecule A is used as a solvent in a variety of applications, including the production of paints, inks, and dyes. It is also used as a humectant in cosmetics and personal care products. Molecule A is also a good nucleophile and can be used to synthesize a variety of new compounds.
- Molecule B:Molecule B is used as an alkylating agent in a variety of applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides. It is also used as a solvent in some industrial processes.
Top FAQs
What are the key structural differences between the two molecules?
The two molecules differ in their molecular weight, shape, and the arrangement of their functional groups.
How does the chemical reactivity of each molecule influence their interactions?
The chemical reactivity of each molecule is determined by the presence of specific functional groups. These groups can participate in various chemical reactions, leading to interactions between the two molecules.
What are some potential functional relationships between the two molecules?
The two molecules may exhibit functional relationships in biological systems, such as enzyme-substrate interactions or protein-ligand binding.