Embark on a scientific journey with periodic trends worksheet answers chemistry, an invaluable resource that empowers students to decipher the intricacies of the periodic table. This comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental principles governing the behavior of elements, enabling accurate predictions of their properties and unlocking the secrets of the chemical world.
Through a meticulous exploration of periodic trends, we delve into the fascinating relationships between atomic number, electron configuration, and the physical and chemical characteristics of elements. These trends provide a roadmap for understanding the periodic table, predicting reactivity, and unraveling the mysteries of chemical bonding.
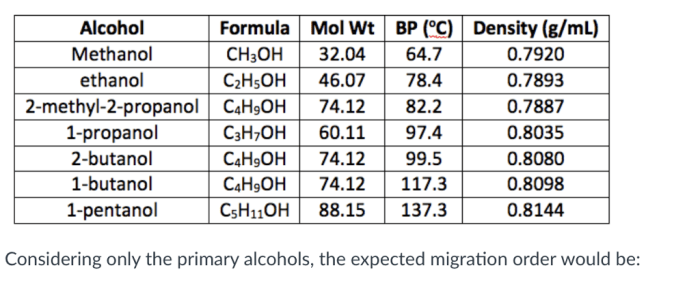
Periodic Table Trends
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Elements are arranged in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) such that elements with similar properties are grouped together.
Periodic trends are the patterns in the properties of elements that can be observed when the periodic table is arranged in this way. These trends can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the table.
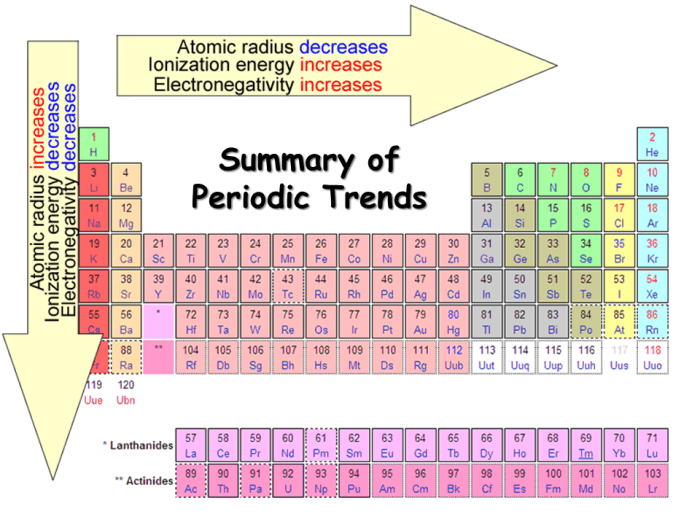
Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to its outermost electron shell. As you move down a group in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases as you move down a group, and the outermost electrons are further away from the nucleus.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases as you move across a period, and the increased nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus.
Ionization Energy, Periodic trends worksheet answers chemistry
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. As you move down a group in the periodic table, the ionization energy generally decreases. This is because the outermost electrons are further away from the nucleus, and are therefore less tightly bound to the atom.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the ionization energy generally increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases as you move across a period, and the increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove an electron.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. As you move down a group in the periodic table, the electronegativity generally decreases. This is because the outermost electrons are further away from the nucleus, and are therefore less tightly bound to the atom.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the electronegativity generally increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases as you move across a period, and the increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult for the atom to attract electrons.
FAQs: Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers Chemistry
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are patterns in the properties of elements that repeat as you move across the periodic table.
How can periodic trends be used to predict the properties of elements?
Periodic trends can be used to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the periodic table. For example, elements in the same group (vertical column) tend to have similar chemical properties.
What are some applications of periodic trends?
Periodic trends have a wide range of applications in chemistry, including predicting reactivity, designing new materials, and understanding chemical reactions.