AP World History Unit 2 MCQ: Embark on a journey through time and explore the captivating civilizations that shaped our world. From the Americas to Europe, this unit delves into the rise and fall of empires, cultural exchanges, and the interconnectedness of human history.
Prepare to unravel the mysteries of ancient civilizations, their achievements, and their lasting impact on the global stage. Dive into the depths of history and emerge with a profound understanding of the past that illuminates the present and inspires the future.
Overview of AP World History Unit 2
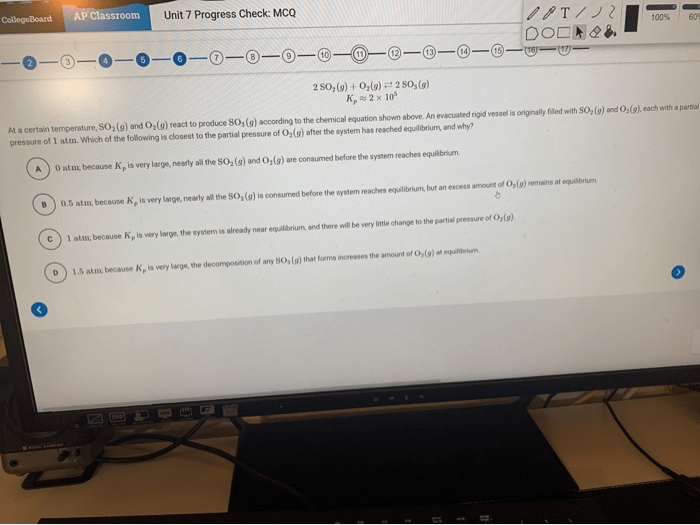
AP World History Unit 2 encompasses a vast chronological expanse, spanning from the late fifteenth century to the early eighteenth century. This era witnessed profound transformations that laid the groundwork for the modern world. The unit delves into the rise of global empires, the spread of new ideas, and the emergence of scientific revolutions that reshaped human understanding and society.
Key themes explored in this unit include the impact of European exploration and colonialism, the development of new technologies and trade networks, and the rise of nation-states. Understanding this historical period is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of global events and the origins of many contemporary issues.
Civilizations in the Americas: Ap World History Unit 2 Mcq

The Americas, a vast and diverse continent, witnessed the rise of several remarkable civilizations that shaped its history and culture. Among these, the Olmecs, Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas stand out as the most prominent, each leaving an indelible mark on the region’s development.
The Olmecs
The Olmecs, the earliest known major civilization in Mesoamerica, flourished from around 1200 to 400 BCE. They are renowned for their monumental stone sculptures, including colossal heads and altars, which depict their rulers and gods. The Olmecs also developed a sophisticated system of writing, mathematics, and astronomy.
The Mayans
The Mayans, who inhabited the Yucatán Peninsula and Central America from around 250 CE to 900 CE, are celebrated for their advanced knowledge in mathematics, astronomy, and writing. They developed a complex system of hieroglyphic writing and created intricate calendars that accurately predicted astronomical events.
The Mayans also built impressive cities with elaborate temples and pyramids, such as Tikal and Chichén Itzá.
The Aztecs
The Aztecs, a powerful empire that ruled central Mexico from the 14th to 16th centuries CE, were known for their extensive trade networks, agricultural innovations, and architectural achievements. They established the city of Tenochtitlan, which was built on an island in Lake Texcoco and became one of the largest and most important cities in the Americas.
The Aztecs also developed a sophisticated system of government and religion.
The Incas
The Incas, who emerged in the Andes Mountains of South America around 1200 CE, established a vast empire that spanned over 2,500 miles. They were skilled engineers who built an extensive network of roads and bridges, as well as impressive architectural structures such as Machu Picchu.
The Incas also developed a unique system of administration and a complex religious system centered around the worship of the sun god Inti.
Interactions and Conflicts
These civilizations often interacted and engaged in both peaceful and conflict-ridden relationships. The Mayans and Aztecs, for example, engaged in trade and cultural exchange, while the Incas conquered and incorporated other Andean civilizations into their empire. However, there were also instances of warfare and territorial disputes, as each civilization sought to expand its influence and control.
Civilizations in Africa
Africa has been a cradle of civilization, with numerous thriving societies emerging across the continent. These civilizations showcased remarkable political, economic, and cultural advancements, shaping the course of African history.
Major Civilizations in Africa
- Kingdom of Aksum (c. 100-940 CE):Located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, Aksum developed a centralized monarchy, a sophisticated writing system, and engaged in extensive trade with the Roman Empire and beyond.
- Ghana Empire (c. 750-1240 CE):Situated in West Africa, the Ghana Empire controlled the trans-Saharan gold trade, accumulating immense wealth and power. It developed a sophisticated system of administration and a centralized bureaucracy.
- Mali Empire (c. 1235-1600 CE):The Mali Empire, also located in West Africa, inherited the wealth and power of Ghana. It expanded its territories and became a major center of Islamic scholarship and trade.
Role of Trade and Commerce
Trade and commerce played a pivotal role in shaping the civilizations of Africa. Trans-Saharan trade routes connected African societies with the Mediterranean world, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. The wealth generated from trade allowed for the growth of cities, the development of crafts and industries, and the rise of powerful empires.
Civilizations in Asia

Asia, the largest continent on Earth, has been home to numerous civilizations throughout history. These civilizations have developed diverse cultures, political structures, and religious beliefs, and have had a profound impact on the world.
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization flourished in the basins of the Indus River in what is now Pakistan and western India from around 2600 to 1900 BCE. It was one of the world’s earliest civilizations, along with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
The Indus Valley Civilization was highly urbanized, with cities such as Harappa and Mohenjo-daro. These cities had well-planned streets, sophisticated drainage systems, and multi-storied buildings. The civilization also had a developed system of writing, although it has not yet been deciphered.
AP World History Unit 2 MCQs can be a breeze if you have the right resources. For example, the article o air and soil whitman provides a comprehensive overview of key concepts. By exploring such materials, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any multiple-choice question on the exam.
Chinese Dynasties
China has a long and rich history of civilization, with the first dynasties emerging around 2000 BCE. Over the centuries, China has been ruled by a succession of dynasties, each with its own unique characteristics.
Some of the most famous Chinese dynasties include the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE), the Tang Dynasty (618 – 907 CE), and the Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644 CE). These dynasties presided over periods of great cultural and economic prosperity, and they left behind a legacy of art, architecture, and literature.
Japanese Civilization
Japan has a unique civilization that has been shaped by its geography and its cultural influences from China and Korea. The first Japanese civilization emerged in the Yayoi period (300 BCE – 300 CE), and it was followed by the Kofun period (300 – 538 CE).
During the Heian period (794 – 1185 CE), Japan experienced a golden age of culture and art. This period saw the development of the Japanese writing system, the creation of masterpieces of literature such as The Tale of Genji, and the emergence of the samurai class.
Cultural Exchanges and Interactions, Ap world history unit 2 mcq
The civilizations of Asia have had a long history of cultural exchanges and interactions. These interactions have led to the spread of ideas, technologies, and religions throughout the continent.
For example, Buddhism spread from India to China and Japan, where it became a major religion. Chinese writing was adopted by Japan and Korea, and it influenced the development of their own writing systems.
Civilizations in Europe
Europe, the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, has been home to a multitude of civilizations throughout history. From the ancient Greeks and Romans to the modern-day nation-states, European civilizations have played a pivotal role in shaping the course of Western civilization.
Greek Civilization
- Emerged in the Aegean region around 2700 BCE.
- Developed a sophisticated system of government, philosophy, and art.
- Made significant contributions to mathematics, science, and literature.
- Laid the foundation for Western civilization through its influence on Roman culture.
Roman Civilization
- Arose in the Italian Peninsula around 753 BCE.
- Established a vast empire that spanned much of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
- Developed a highly organized political system, a sophisticated legal code, and an extensive network of roads and aqueducts.
- Spread Christianity throughout the empire, which later became the dominant religion in Europe.
Impact on Western Civilization
The Greek and Roman civilizations had a profound impact on Western civilization. Their political ideas, philosophical concepts, and artistic achievements continue to influence Western culture today. The Roman Empire’s legal system, infrastructure, and administrative practices laid the groundwork for many modern European institutions.
The spread of Christianity by the Romans shaped the religious landscape of Europe and played a major role in the development of Western civilization.
Interactions and Connections
The civilizations of the world did not develop in isolation. Throughout history, they have interacted and connected with each other in various ways, leading to the exchange of ideas, technologies, and cultures. These interactions have shaped the development of global history.Trade,
migration, and cultural diffusion were the primary drivers of these interactions. Trade routes, such as the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between civilizations. Migration, driven by factors such as war, famine, or economic opportunities, brought people from different regions together, leading to the spread of cultures and technologies.
Cultural diffusion occurred through the spread of ideas, beliefs, and practices from one civilization to another, often through contact between traders, travelers, or missionaries.
Trade
Trade played a crucial role in the interactions between civilizations. It facilitated the exchange of goods, such as spices, textiles, and luxury items, as well as the spread of technologies and ideas. The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting China with the Mediterranean Sea, was a major conduit for the exchange of goods and ideas between East and West.
Migration
Migration was another important factor in the interactions between civilizations. People migrated for various reasons, including war, famine, economic opportunities, or religious persecution. Migration led to the spread of cultures and technologies, as people brought their own traditions and practices to their new homes.
For example, the Bantu migrations in Africa spread ironworking technology and agricultural practices throughout the continent.
Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion occurred through the spread of ideas, beliefs, and practices from one civilization to another. This could happen through contact between traders, travelers, or missionaries. For example, the spread of Buddhism from India to China and Japan was a major example of cultural diffusion.
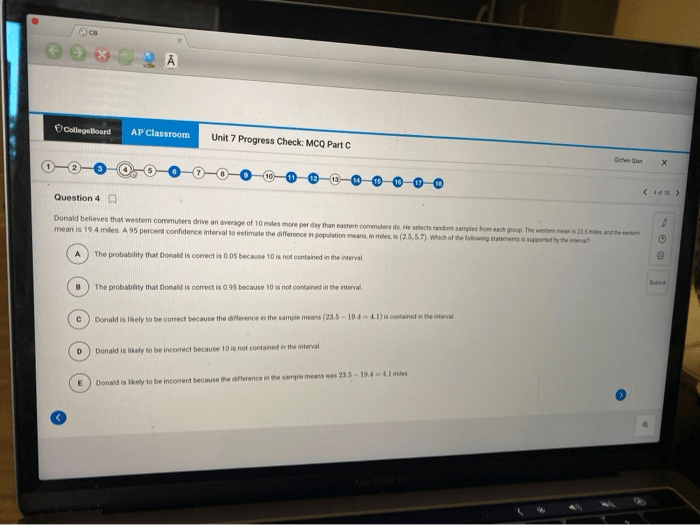
Clarifying Questions
What is the time period covered by AP World History Unit 2?
Unit 2 covers the period from c. 600 BCE to c. 1450 CE.
What are the key themes explored in this unit?
Key themes include the development of civilizations, cultural interactions, economic systems, political structures, and the impact of the environment on human societies.
Why is it important to understand this historical period?
Understanding this period provides a foundation for comprehending the origins and evolution of global events and the interconnectedness of human history.