Embark on an interactive journey with drag and drop each characteristic to the correct tissue type., an innovative approach that empowers you to grasp the intricacies of human tissues. This engaging tool unveils the diverse nature of tissues, their specialized functions, and the remarkable ways they orchestrate to form complex organs and organ systems.
Delve into the structural characteristics that distinguish each tissue type, unraveling the secrets of their cellular composition, extracellular matrix, and functional capabilities. Prepare to witness the dynamic organization of tissues, from the fundamental level of cells to the intricate interplay within organs and organ systems.
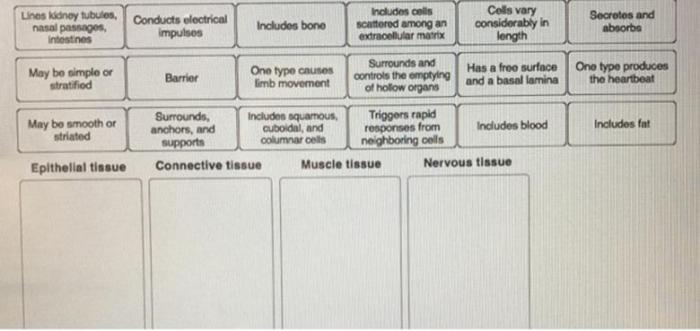
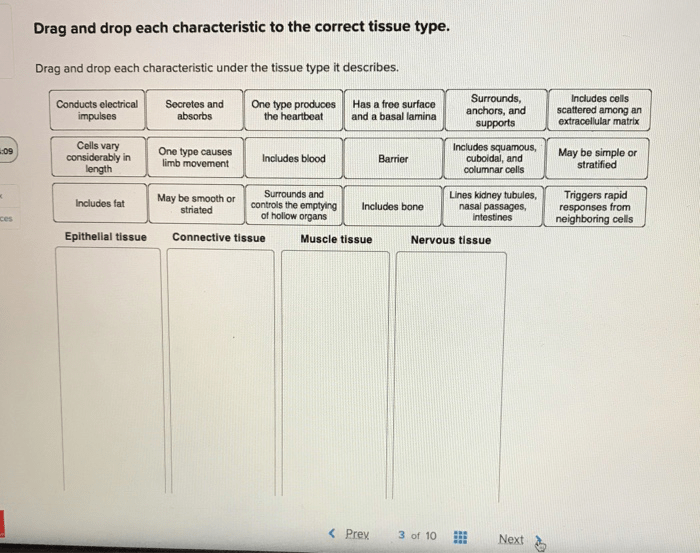
Tissue Types: Drag And Drop Each Characteristic To The Correct Tissue Type.

Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
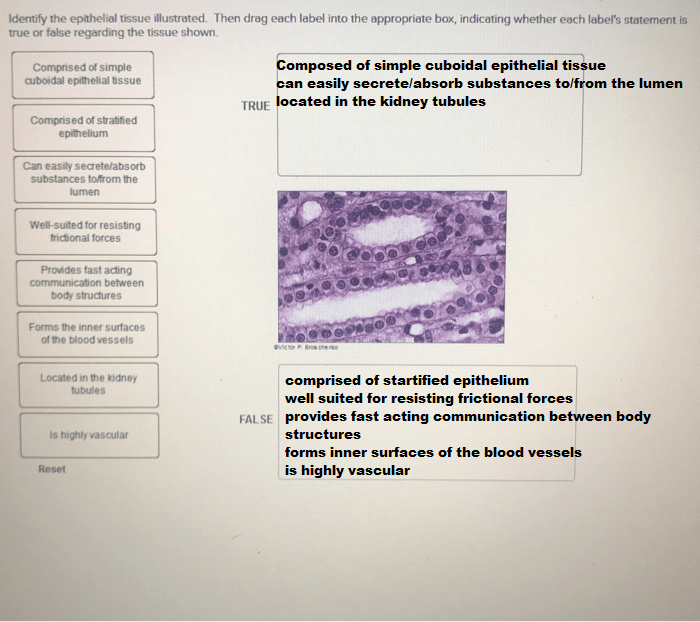
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body. It protects the body from the environment and helps to regulate the passage of substances into and out of the body.
- Cells are closely packed together with little extracellular matrix.
- Has a basement membrane that separates it from the underlying connective tissue.
- Functions include protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects the other tissues of the body. It is made up of cells that are embedded in a matrix of extracellular material.
- Cells are widely spaced and embedded in a matrix of extracellular material.
- Matrix can be fluid, semi-solid, or solid.
- Functions include support, protection, storage, and transport.
Muscle Tissue, Drag and drop each characteristic to the correct tissue type.
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It is made up of cells that contain specialized proteins that allow them to contract.
- Cells are long and thin with a striated appearance.
- Contains contractile proteins actin and myosin.
- Functions include movement, posture, and heat production.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is responsible for communication within the body. It is made up of cells that are specialized for the transmission of electrical signals.
- Cells include neurons and glial cells.
- Neurons have long extensions called axons and dendrites.
- Functions include communication, coordination, and control.
FAQ Summary
What are the key structural characteristics used to classify tissues?
Cell shape, extracellular matrix composition, and functional specialization are the primary criteria for tissue classification.
How does tissue organization contribute to organ function?
The specific arrangement and coordination of tissues within an organ determine its overall function and efficiency.
What factors influence tissue repair and regeneration?
Age, injury type, overall health, and genetic factors all play a role in shaping the tissue repair process.